
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Result
- Report
Convert Your Score To GPA
The Grade Point Average (GPA) stands as a pivotal metric for assessing academic performance, predominantly in North America but also recognized in various other nations, albeit with differences in grading systems and associated methodologies. While students within the United States typically present their transcripts directly when applying for higher education, international applicants face the additional task of converting their academic grades into the GPA format, which serves as the standardized grading scale in the US. This conversion process ensures equitable evaluation and comparison of academic achievements for international candidates, aligning them with domestic applicants and facilitating a fair assessment within the US educational landscape.

What is the Grade Point Average?
Grade Point Average serves as a numerical representation of a student’s overall academic performance. This calculation involves assigning a numerical value to each letter grade received in a course and then averaging those values. Typically ranging from 0.0 to 4.0, with 4.0 being the highest achievable score, the Grade Point Average scale assigns values such as 4.0 for an A, 3.0 for a B, 2.0 for a C, 1.0 for a D, and 0.0 for an F (fail). Educational institutions employ Grade Point Average to determine academic standing, scholarship eligibility, and admission into higher education programs. Additionally, it serves as a measure of academic qualifications and potential in the job market.
Why is Grade Point Average important?
Grade Point Average (GPA) is an important metric that is widely used to measure a student’s academic performance. Here are some reasons why GPA is important:
- Academic Standing: Grade Point Average is often used by educational institutions to determine a student’s academic standing. A student with a higher Grade Point Average is generally considered to have performed better academically than a student with a lower Grade Point Average.
- Eligibility for Scholarships and Awards: Many scholarships and awards are based on Grade Point Average. Students with higher Grade Point Averages are often given priority consideration for scholarships and awards, as they are perceived to have demonstrated greater academic achievement and potential.
- Admission to Higher Education Programs: Grade Point Average is often used as a criterion for admission to higher education programs such as colleges and universities. Many institutions have minimum GPA requirements for admission, and a higher GPA may increase the chances of acceptance into a competitive program.
- Job Market: GPA is also used in the job market as a measure of a candidate’s academic qualifications and potential. Some employers may consider a candidate’s Grade Point Average as an indicator of their work ethic, discipline, and attention to detail.
- Professional Licensing and Certifications: Certain professions, such as law, medicine, and accounting, require individuals to obtain professional licenses or certifications. GPA may be a factor considered during the licensure or certification process, especially for competitive fields.
- Transfer Opportunities: If you plan to transfer to another institution during your academic career, your Grade Point Average can influence your chances of admission to your desired transfer institution. Higher GPAs may open doors to transfer scholarships or admission to selective institutions.
- Employer Education Assistance Programs: Some employers offer education assistance programs to support their employees’ continued education or professional development. GPA may be a consideration when applying for these programs or seeking reimbursement for educational expenses.
- Academic Honors and Recognition: Many schools offer academic honors, such as Dean’s List or honors societies, based on Grade Point Average thresholds. Achieving a high Grade Point Average can lead to recognition for your academic achievements within your institution.

How is GPA calculated?
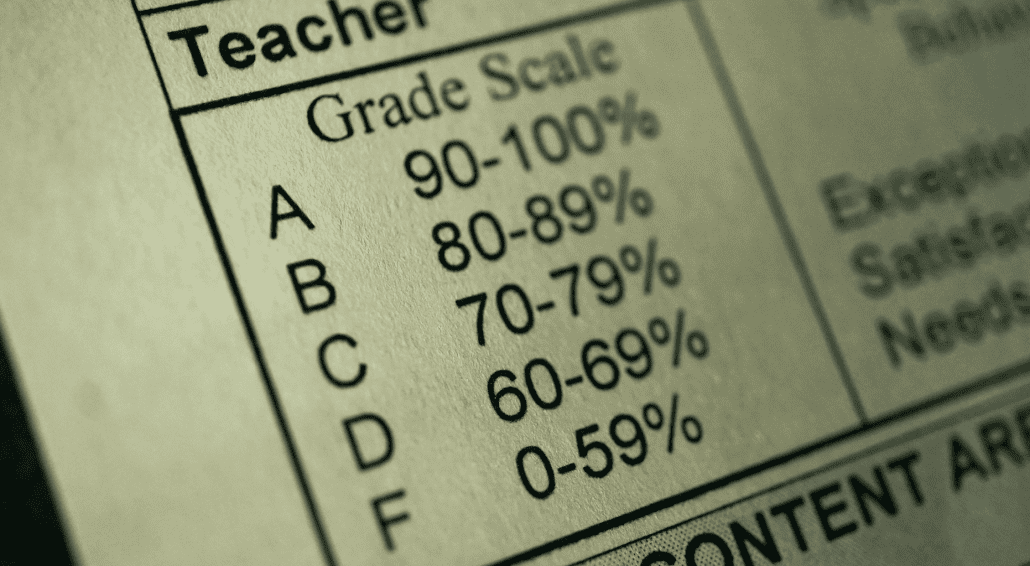
In the US, grades are assigned on a scale from 0 to 4, with 4 denoting an A and 0 denoting an F. To calculate a candidate’s grade point in the US, the candidate’s total number of credits or hours of the course is multiplied by the grade equivalent (4 if the candidate received an A). The GPA is calculated by dividing this grade point by the total number of units the candidate has taken this semester. The following table lists the grade equivalents of each possible course grade a candidate could receive, along with the corresponding percentage equivalent.
| Grade Points | Grade range | Equivalent |
| 0 | F | <60% |
| 1 | D | 60-69% |
| 2 | C | 70-79% |
| 3 | B | 80-89% |
| 4 | A | 90-100% |
The grades listed above are the most transformed data of the grading scheme, but some grades and equivalents fall in between them. These grades are
| Grade | Grade Point |
| F | 0 |
| D- | 0.67 |
| D | 1.00 |
| D+ | 1.33 |
| C- | 1.67 |
| C | 2.00 |
| C+ | 2.33 |
| B- | 2.67 |
| B | 3.00 |
| B+ | 3.33 |
| A- | 3.67 |
| A | 4.00 |
Grade Point Average system worldwide
The Grade Point Average system is widely used around the world, but the specific calculation method and grading scales can vary depending on the country and educational system. Here are some examples of how the GPA system is used in different parts of the world:
- United States: In the US, the Grade Point Average scale ranges from 0.0 to 4.0, with 4.0 being the highest achievable Grade Point Average. In some cases, weighted Grade Point Averages can be used, which gives extra points for grades in advanced or honors courses.
- Canada: In Canada, GPAs are typically calculated on a scale of 0.0 to 4.3, with 4.3 being the highest achievable GPA. Some universities in Canada also use a percentage-based grading system.
- Europe: In many European countries, GPAs are calculated on a scale of 0.0 to 10.0, with 10.0 being the highest achievable Grade Point Average. However, grading scales can vary by country and even by institution.
- Australia: In Australia, Grade Point Averages are typically calculated on a scale of 0.0 to 7.0, with 7.0 being the highest achievable score.
- Asia: In some Asian countries, such as India and China, GPAs are calculated on a scale of 0.0 to 10.0, similar to the European system. However, grading scales can vary widely between institutions.
It’s important to note that while the GPA system is widely used around the world, it is not the only method of grading. Some countries and educational systems use different grading scales or other methods of evaluation, such as numerical grades or letter grades without corresponding GPA values. It’s always a good idea to familiarize yourself with the grading system used in the country or institution you are studying in to understand how your academic performance is being evaluated.
GPA Score in Universities
One of the crucial criteria for admission to a reputable college is GPA. Candidates can enter the top 50 colleges with a higher GPA and above-average GRE/SAT scores. A candidate’s admission to one of the top 20 colleges in the nation may be contingent on their class rank. The GPA serves as a clear indicator of one’s academic performance and demonstrates the candidate’s aptitude for academic success. This is also true because tests like the GRE and SAT/ACT do not evaluate a person’s academic abilities, even though it is frequently believed that applicants with high GRE or SAT scores will also have high GPAs. The courses a student has taken, their Grade Point Average, class rank, and SAT/ACT scores are all significant factors for undergraduate students.
For admission to a graduate program, most universities have a minimum GPA requirement of at least 3/4. The minimum threshold for a Ph.D. is much higher than 3/4. For international students, the GPA calculation may be different. Moreover, there are other requirements for admission besides GPA. If the rest of their college application is strong, applicants with low GPAs can still get into reputable universities.
Calculating your Grade Point Average (GPA) is a straightforward process that helps you understand your academic performance about the grading standards of your educational institution. Here’s a simplified explanation along with a step-by-step guide and examples to help you accurately determine your GPA.
How to Calculate Your GPA
To calculate your GPA, you need to follow these steps:
- List Each Course with Corresponding Grade and Credit Hours: Start by listing each course you’ve taken, along with the grade received and the credit hours for the course. Each grade is assigned a grade point value, which varies depending on your school’s grading system.
- Convert Grades to Grade Points: Convert each grade into a grade point using your institution’s scale. For instance, on a typical scale:
- A = 4.0
- B+ = 3.3
- B = 3.0
- C+ = 2.3
- C = 2.0
- D = 1.0
- F = 0.0
- Calculate Total Grade Points for Each Course: Multiply the grade point for each course by its respective number of credit hours.
- Sum Up All Credit Hours and Total Grade Points: Add up all the credit hours and all the grade points separately.
- Divide Total Grade Points by Total Credit Hours: Divide the total grade points by the total credit hours to get your GPA.
Examples
Example 1:
- Biology: B+ (3.3) | 3 credits | 3 x 3.33 = 9.99
- Physics: C (2.0) | 6 credits | 6 x 2.00 = 12.00
- Mathematics: A- (3.7) | 3 credits | 3 x 3.67 = 11.01
- Total Credits: 12
- Total Grade Points: 33.00
- GPA Calculation: 33.00 ÷ 12 = 2.75
In this example, the GPA is 2.75, suggesting an overall B to B- average.
Example 2:
- Biology: F (0.0) | 3 credits | 3 x 0.00 = 0.00
- Physics: A- (3.7) | 3 credits | 3 x 3.67 = 11.01
- Mathematics: C (2.0) | 6 credits | 6 x 2.00 = 12.00
- Arts: B+ (3.3) | 3 credits | 3 x 3.33 = 9.99
- Total Credits: 15
- Total Grade Points: 33.00
- GPA Calculation: 33.00 ÷ 15 = 2.20
In this second example, the GPA is 2.20, indicating an average grade between C+ and C.
By following these steps and using the examples as guides, you can accurately calculate your GPA and gain better insight into your academic performance.
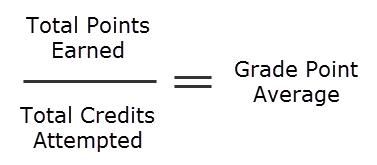
Frequently Asked Questions: Grade Point Average (GPA)
Yes. Transfer courses (T-series course numbers T05, T10, T20) are included in the GPA calculations.
All courses with the “Include in GPA” flag are included in GPA calculations for the Academic GPAs. All courses are included in the Athletic GPA calculations.
Grades with the final grade scale indicator “NoNumericEquiv” will not be considered when calculating GPA. The following grades currently have No Numeric Equivalent: P (P is included in the Athletic GPA), I, UN, and MFG.
If a student receives one of the ignored final grades, their record will not be taken into account when calculating their GPA, even if a course is marked with the “Include in GPA” checkbox.
When the Grade Point Averages Report is run, and the option to Update GPA on Student Record is chosen, the student’s GPA is updated.
When there is a change to the student transcripts, a GPA will be updated if your Grade Preferences (School>Set up>Preferences>Grades category) setting is set to Auto-Calculate either Force or Enable-Checked (a grade change or new transcript record added).
The Student GPA fields won’t reflect the change. The Grade Point Summary for the academic year in which the change was made will reflect the change. When the option to Update the student table is chosen when running the Grade Point Averages Report again, the student GPAs will be updated.
Before transcript change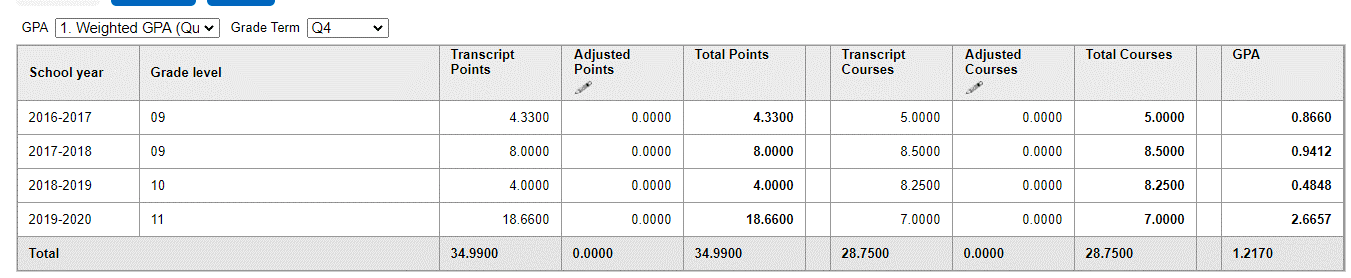
After transcript change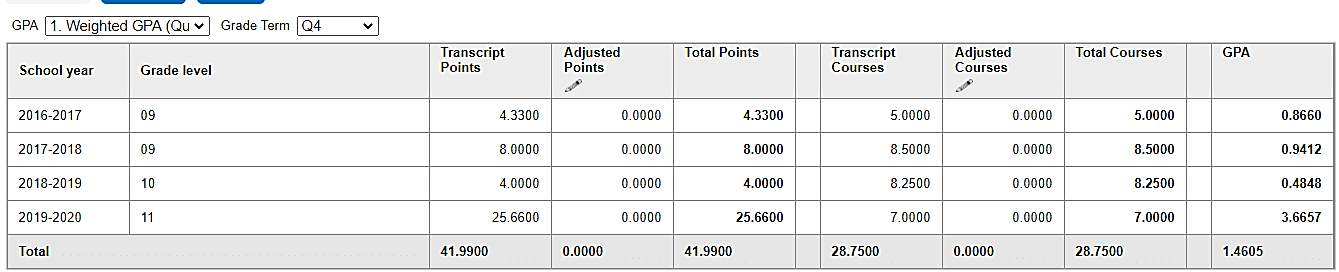
The course will be counted toward the GPA if it is marked with the “Include in GPA” flag.
The class rank is determined by a formula that considers a student’s grade point average (GPA), a multiplier of credits earned, and bonus points given to particular coursework levels. Each student receives a class rank value as a result of the formula. These values are then compared to the student population in each grade, resulting in a rank order that indicates each student’s position within their graduating class. A student’s GPA is multiplied by the total number of credits earned to determine their class rank, and additional points are added for taking certain courses designated as electives.
The system counts the number of active students in each Year of Graduation when the Grade Point Averages Report is run with the option set to recalculate (not grade level). The “Out of number” in the class rank is this number, which is stored.
All students are included when running the Grade Point Averages Report, which will produce the student ranking.
Employers might inquire about your GPA if they anticipate receiving applications from recent graduates with little work experience. For instance, if they are hiring for an entry-level position, they might require a GPA on the application to help them select applicants.
Depending on the employer and the sector you intend to work in, it will differ. Their questions about your educational background center on whether you have a degree in a relevant field once you have advanced in your career and gained professional experience.
When a candidate has a high GPA, which many experts define as 3.5 to 4.0, they frequently include it in their application. A GPA in that range can show potential employers that you are dedicated to your studies and have worked hard. The average GPA ranges from 3.0 to 3.4, but some employers advise including any GPA at least 3.0.
If you are a current student or a recent graduate (within the last three years) of a college or high school and your GPA is higher than 3.5, you should include it. Employers occasionally specifically request applicants’ GPAs, so you must include them on your application regardless of their value. Employers might assume that you did not read the instructions carefully or that you did not want to display your GPA because it was low if you failed to include it after being asked to do so.
You can remove your GPA from your resume once you’ve had at least three to five years of professional work experience. By that time, you have established a track record of success in your industry, so employers are no longer dependent on your GPA to gauge your commitment to your work.
While some employers may request your GPA, most won’t use it as their only factor in hiring. Unless specifically requested, you don’t have to include it if it makes you uncomfortable. To highlight your strengths as a student, you can highlight other academic accomplishments you have received.
Your resume or application should also highlight your relevant experiences and abilities, proving that you are qualified to carry out the position’s responsibilities. Employers will be impressed by your abilities because they demonstrate that you can handle pertinent tasks and may not need extensive training to begin working.
Your GPA is probably not going to come up during the interview process. Examine the job description and ensure you bring examples showing you possess the skills the employer has listed.
If you anticipate being asked questions about your GPA, be prepared to explain how you overcame or handled any academic challenges. Employers will be grateful if you can describe how you take the initiative to better yourself when necessary.
You must still be truthful when asked to include your GPA, even if you think it is lower than what the employer expects or requires. Hiring managers may use your transcript to confirm your GPA during the background check procedure. Your chances of landing the job could be harmed if it is found that you provided an incorrect number. Additionally, you make an effort to include any pertinent accolades or accomplishments from your academic career to support the education section.
Simply follow the steps below to calculate your weighted GPA:
Step 1: Convert every letter grade to its respective points (A=4, B=3, C=2, D=1, F=0.)
Step 2: Add up all the grade points
Step 3: Divide the added grade points (step 2) by the number of class credits taken.
Note: For Honors and AP classes, you should give yourself one additional point for every semester of an Honors or AP class that you have completed (A=5, B=4, C=3.)
A student’s overall grade point average (GPA) is determined by dividing their total grade points from all semesters by the total number of credits taken. Compared to a semester or year GPA, the resulting average provides a more complete picture of a high school or college career.
The grade that colleges and employers typically consider is the cumulative GPA. It provides a long-term perspective and demonstrates a strong track record of academic success, making it a crucial indicator of consistency. After all, a student who enrolls in easy classes in the second half of their junior year might earn all “A”s that semester, but a total that accounts for points earned throughout the entire academic career is more accurate.
