Study in Turkey For International Students Free in 2024-2025
Turkey has dedicated considerable efforts to enhance its education sector in the past decade, creating a compelling and accessible environment for students from neighboring countries and worldwide. The nation has swiftly gained recognition, hosting 108,000 international students representing over 180 countries in its diverse tertiary institutions.
The Turkish education system features state-of-the-art universities with exceptional intellectual capabilities, complemented by top-tier educational facilities nationwide. Turkish educational institutions provide various programs at the post-secondary level, ranging from undergraduate associate degrees to postgraduate doctoral degrees.
Turkey offers a rich educational landscape with 166 universities in the registered catalog, 104 publicly owned. Government universities predominantly use the Turkish language, requiring international students to undergo a year of pre-university Turkish language instruction before commencing formal programs. Conversely, private universities often conduct courses in English.
Tuition fees in Turkey are notably affordable, especially at public universities, where costs can range from $240 to $750 in Turkish and $600 to $1,500 in English per academic year. Private institutions generally have higher fees, varying from $6,000 to $20,000 annually. Most private institutions mandate international students to receive scholarships ranging from 10 to 50 percent to alleviate financial burdens. Postgraduate courses typically incur tuition fees between $300 and $1,000 per academic year. Turkey follows a two-semester calendar, alternating between fall and spring.

While offering various academic fields, common courses for international students encompass engineering, international relations, multicultural affairs studies, medicine, business management, hospitality, tourism, architecture, eastern Mediterranean studies, law, and pharmacy.
The duration of academic studies in Turkish universities aligns with global tertiary standards. Associate degrees span two years, undergraduate programs extend for three to four years (with the option of summer school to expedite the timeline), master’s programs last one to two years, and doctoral programs require three to four years. Program durations may vary based on specific requirements, internships, and other factors.
Turkey Details
The Turkish Republic, formerly the Ottoman Empire, is a cutting-edge, explosive powerhouse established in 1923 and is regarded as a part of Asia and Europe. The predominantly Muslim nation borders Greece and Bulgaria to the west, Russia, Ukraine, and Romania to the north and northwest (via the Black Sea), Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east, and Syria and Iraq to the south. It also has access to the Aegean, Black, and Mediterranean seas.
As one of the founding members of both the United Nations and the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, the country has long been committed to global advancement (OECD).
As evidenced by numerous historical monuments and locations that have grown to be major tourist attractions and ways in which the nation has thus been able to tell its history, Turkey is a diverse and multicultural nation boasting an extensive heritage. Despite being predominately Muslim, Turks are renowned for being a warm, amiable, and welcoming nation.
It is common to find Mediterranean and Asian influences in Turkish culture and society, particularly in food, fashion, and lifestyle. Turkey is notable for being where the East meets the West; as a result, its culture is incredibly rich and influenced by neighboring countries. Turkish is Turkey’s most widely used language, but Arabic and Latin have also impacted the nation. English is also slowly becoming more widely used due to school westernization efforts.
Turkey has incredible landscapes, including untamed mountains, wild forests, and beautiful beaches along its coasts. Turkish cities are well-known for their distinctive architectural designs and long histories. Istanbul, the country’s capital, is a stunning city with many amazing features, including popular tourist attractions like the Blue Mosque, the Bosphorus Bridge, and the Topkapi Palace, well-known sporting venues like Galatasaray and Fenerbache, fantastic shopping and nightlife experiences, and fantastic locations for living, working and studying.
Turkey’s hospitable climate is perfect for summer travel and somewhat chilly winters. Summer temperatures in inland areas are typically higher than in coastal cities. On average, Istanbul experiences summertime highs of about 29 C and wintertime lows of about 3 C. Ankara’s average minimum temperature is -7 C, while the maximum average temperature in the Mediterranean and Southeast Anatolia regions is 35 C.
The housing options provided to new students are first-rate, cutting-edge, and unquestionably in a class by themselves, in keeping with the rest of the nation’s advanced infrastructure. Apartment types available on campus include single, double, triple, and quadruple units. Universities offer a wide range of custom apartments and rooms, so living arrangements and costs depend on the student’s specific needs, the location of these facilities, and the type of accommodation arrangement. On average, prices range from $1.500 to $3.600 per academic year on campus and from $2.400 to $6,000 off campus.
Even though accommodations can vary, some of the most common amenities include Wi-Fi, in-room air conditioning, flat-screen TVs, and 24-hour security. Most of Turkey’s coastal areas enjoy a lovely Mediterranean climate, which goes well with the gorgeous beach scenery students can enjoy in the summer. The seasons change the weather, with some regions experiencing wet winters and dry summers while others experiencing bitterly cold winters and sunny, dry summers.
Turkish Economy
Turkey has a mixed economy with a combination of modern industry and commerce and a more traditional agriculture sector. It is classified as an emerging market and ranks among the world’s top 20 economies by nominal GDP. Here are some key aspects of the Turkish economy:
- Diversified Sectors:
- Agriculture: While the agriculture sector has seen a decline in its contribution to GDP, it still plays a role in the economy, particularly in rural areas.
- Industry: Turkey has a strong industrial sector, including manufacturing, automotive, textiles, and electronics.
- Services: The services sector, including tourism, finance, and real estate, has significantly contributed to the economy.
- Export-Driven Economy:
- Turkey has been reliant on exports for economic growth. Key export items include machinery, textiles, automotive products, and chemicals.
- Geopolitical factors and global economic conditions can impact the country’s export performance.
- Tourism:
- Tourism has traditionally been a crucial sector of the Turkish economy. The country attracts millions of visitors annually due to its rich historical and cultural attractions.
- Currency and Inflation:
- The Turkish lira (TRY) is the official currency. Turkey has faced inflation, currency devaluation, and monetary policy challenges.
- Government Policies:
- The government has implemented various economic reforms to attract foreign investment and enhance economic stability.
- Political and economic policies can significantly affect investor confidence and economic performance.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Infrastructure projects, including transportation and energy initiatives, have been a focus of government efforts to support economic growth.
- Challenges:
- Turkey has faced economic challenges, including high inflation, a large current account deficit, and currency volatility.
- Geopolitical tensions and uncertainties can impact investor confidence.

Why Study in Turkey
Turkey has been an increasingly popular destination for international students, offering a range of benefits that make it an attractive choice for higher education. Here are some reasons why students may choose to study in Turkey:
- Cultural Richness:
- Turkey has a rich cultural heritage with a blend of Eastern and Western influences, making it an appealing destination for those interested in history, art, and diverse traditions.
- Historical and Architectural Wonders:
- The country is home to numerous historical and architectural wonders, including Hagia Sophia, the Blue Mosque, and Ephesus, providing students with unique exploration and cultural immersion opportunities.
- Affordable Living Costs:
- Compared to many Western countries, the cost of living in Turkey is relatively affordable. This includes accommodation, food, and transportation.
- Quality Education Institutions:
- Turkey has several reputable universities and academic institutions that offer a wide range of programs in various fields. Some of these universities are gaining international recognition.
- Diverse Landscape:
- Turkey boasts a diverse and picturesque landscape, from bustling cities to beautiful coastlines and mountains. This diversity provides students with various experiences outside of their academic pursuits.
- Multicultural Environment:
- Turkey is a melting pot of cultures with a history of being a bridge between Europe and Asia. Studying in such an environment can expose students to different perspectives and foster a multicultural experience.
- Language of Instruction:
- Many programs in Turkey are offered in English, especially at the postgraduate level, making it accessible to international students who may not be fluent in Turkish.
- Hospitality and Warmth:
- Turkish people are known for their hospitality and warmth. International students often find the local population to be friendly and welcoming.
- Gateway to Europe and Asia:
- Geographically situated at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, Turkey offers students the opportunity to explore neighboring regions and gain a broader perspective.
- Opportunities for Research and Innovation:
- Turkish universities are increasingly focusing on research and innovation, providing students with opportunities to engage in cutting-edge projects and contribute to advancements in various fields.
- Scholarship Opportunities:
- The Turkish government and various institutions offer scholarships to international students, easing the financial burden of studying abroad.
Scholarships to Study in Turkey
there are various scholarship opportunities available for international students to study in Turkey. The Turkish government, universities, and other institutions offer these scholarships. It’s important to note that scholarship programs and eligibility criteria may change, so checking the latest information from official sources is advisable. Here are some scholarship options in Turkey:
- Turkish Government Scholarships:
- The Türkiye Scholarships program is a government-funded initiative that provides scholarships to international students for undergraduate, graduate, and doctoral studies in Turkey. It covers tuition fees, accommodation, health insurance, and a monthly stipend.
- Turkish Universities Scholarships:
- Many Turkish universities offer their scholarship programs for international students. These scholarships may cover tuition fees, accommodation, or living expenses. Check with the specific university you are interested in for available opportunities.
- Research Scholarships:
- Some scholarships are specifically designed for research-oriented programs. Research institutions, foundations, or government agencies may offer these to support students pursuing research projects in Turkey.
- Turkish Language Scholarships:
- Plan to study a program in Turkish. You may find scholarships that cover Turkish language courses to help international students improve their language skills before starting their academic programs.
- Cultural Exchange Programs:
- Organizations such as the Yunus Emre Institute and the Turkish Cultural Foundation offer cultural exchange programs that may include language and cultural studies scholarships.
- Bilateral Agreements:
- Some countries have bilateral agreements with Turkey that include scholarship programs for students. Check with your home country’s education ministry or relevant authorities for information on such agreements.
- Business and Industry Scholarships:
- Certain industries and businesses in Turkey may offer scholarships to international students pursuing fields related to their sector. Private companies or industry associations may sponsor these scholarships.
- International Organizations and Foundations:
- Some international organizations and foundations may provide scholarships to students from specific regions or backgrounds. Explore opportunities offered by organizations that support education and cultural exchange.
Turkey Student Visa
The process for obtaining a student visa for Turkey involves several steps. Please note that visa procedures can be subject to change, and it’s essential to consult the official website of the Turkish consulate or embassy in your country for the most up-to-date information. Here is a general overview of the steps involved:
- Acceptance to a Turkish University:
- Before applying for a student visa, you must secure admission to a Turkish university or educational institution. Typically, you will receive an acceptance letter, which is a crucial document for the visa application.
- Get a Pre-Application Appointment:
- Visit the official website of the Turkish consulate or embassy in your home country and schedule a pre-application appointment. This appointment is usually conducted online.
- Prepare Required Documents:
- Gather all the necessary documents for your visa application. These typically include:
- Visa application form
- Passport-sized photos
- Passport (with a validity of at least six months beyond your intended stay)
- Acceptance letter from the Turkish university
- Proof of financial means to cover living expenses
- Proof of accommodation in Turkey
- Health insurance coverage
- Flight reservation
- Visa application fee receipt
- Gather all the necessary documents for your visa application. These typically include:
- Attend the Appointment:
- Attend the pre-application appointment at the Turkish consulate or embassy. During the appointment, you may be required to submit your documents, provide biometric data (such as fingerprints), and pay the visa application fee.
- Wait for Visa Processing:
- After submitting your application, the embassy or consulate will process your visa. The processing time can vary, so applying well before your travel date is advisable.
- Receive Visa Decision:
- Once your visa is processed, you will receive a decision. If approved, the visa will be stamped on your passport.
- Travel to Turkey:
- With a valid student visa, you can travel to Turkey. Ensure you enter the country within the specified period mentioned on your visa.
- Residence Permit in Turkey:
- After arriving in Turkey, you must apply for a residence permit within the first month. This permit allows you to stay in the country for your studies.
Study in Turkey: Top universities in Turkey
In the 2022 edition of the QS University Rankings: EECA, which ranks the top universities in Emerging Europe and Central Asia, there are 45 and 10 Turkish universities. The two largest cities in Turkey, Ankara and Istanbul, are home to most of these top universities. The top 50 universities in Ankara are Middle East Technical University, Bilkent University, and Hacettepe University, while the top 30 universities in Istanbul are Boaziçi Üniversitesi, Koç University, Sabanc University, Istanbul Technical University, and Istanbul University.

1-Middle East Technical University (METU)
Middle East Technical University (METU), which has its headquarters in Ankara, the capital of Turkey, rose one spot this year to take eighth place in the EECA rankings. It was established in 1956, focusing on the natural and social sciences to play a crucial role in developing Turkey and other Middle Eastern nations. Today, it has about 31,000 students, many exchange students studying there for a semester or an entire year.
Due to the high demand, METU only accepts students from the top 1.5% of its 1.5 million applicants yearly. English is used as the instruction language.

2-Boğaziçi Üniversitesi
Boaziçi Üniversitesi, currently ranked in the top 10 universities (in 10th place), was founded in 1863 as Robert College and was the first American university to be established outside of the United States. The historic castle of Rumelihisar, which flanks the eastern edge of the university’s South Campus, and the Bosphorus strait are both near Boaziçi Üniversitesi’s Istanbul location. The university maintains close ties to the American higher education system and offers courses in English, just like Middle East Technical University.
3- Koç University
Koç University, established in Istanbul in 1993 and currently ranked 12th in the EECA region, bears the name of its founder, the businessman and philanthropist Vehbi Koç. With 22 undergraduate, 32 graduate, and 18 Ph.D. programs, Koç University, one of Turkey’s most prestigious universities, provides a top-notch educational experience to its approximately 5,500 students. “To cultivate Turkey’s most competent graduates, well-rounded adults who are internationally qualified; who can think creatively, independently, and objectively; and who are confident leaders,” the university’s mission statement reads.
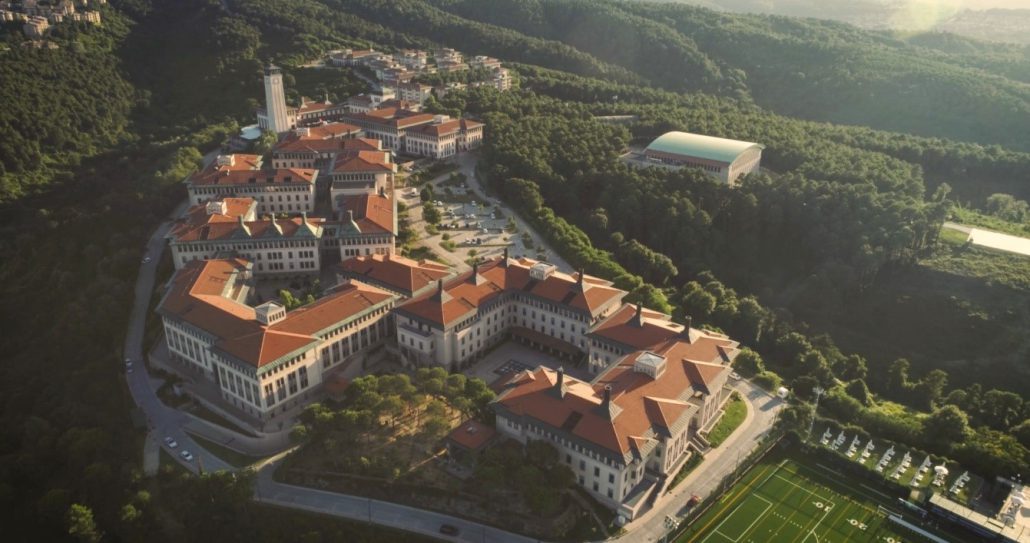

4- Bilkent University
The name Bilkent University is an acronym for “bilim kenti,” which is Turkish for “city of learning and science,” and is ranked 14th in the 2019 EECA rankings. The most comprehensive academic library in the nation is found at Bilkent University, established in 1984 by Turkish academician Hsan Doramac. One of the top research-intensive universities in the country, it currently enrolls about 13,000 students across nine faculties and two four-year professional schools, many of whom are from abroad.
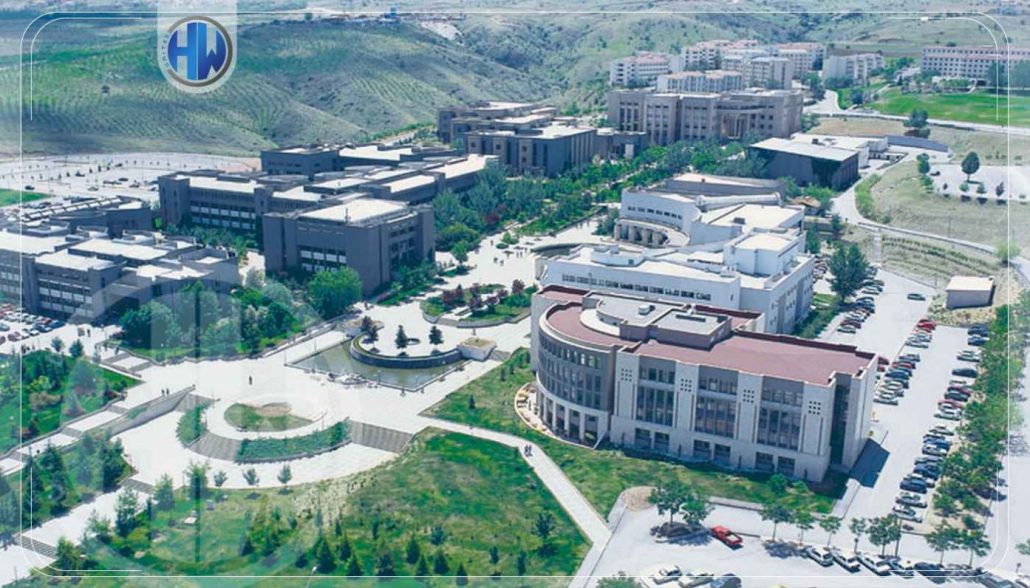

5- Sabanci University
In the EECA rankings this year, Sabanci University, which is also in Istanbul, is ranked in 18th place and is the fifth-highest university in Turkey. It is a new university that only started offering classes in the fall of 1999. There are currently about 4,000 students enrolled there. Both the Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences (FASS) and the Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences (FENS) at Sabanci University offer their students a wide range of disciplines at the undergraduate and graduate levels. Scholarships are awarded to about 42% of its undergraduate students.
Frequently Asked Questions: Study in Turkey
Turkish language study is optional at universities where English is the primary language of instruction. However, this course will greatly improve international students’ experience living in Turkey.
Given that each has a different application process, this should be decided before applying. If your current home university and your desired university in Turkey have a bilateral agreement, you are an Erasmus exchange or exchange student. You apply to your home university. Please contact the exchange office at your home university if you have any questions about your eligibility.
If you submit an independent application or your home university agrees to cover the cost of your stay at the Turkish university of your choice, you are a special student.
Before applying to a Turkish university, you must receive a nomination from your home institution.
Each host institution has its own set of admission requirements. The selection process will consider one’s academic history, language proficiency, and other factors.
Once you have your acceptance letter, contact the Turkish Consulate, most conveniently located in your nation, to apply for a student visa. Between 15 and 45 days may pass during the procedure. Within 30 days of your arrival, you must apply for a residence permit. By doing this, you can enter and exit Turkey without applying for a visa again.
Yes, many Turkish universities are globally recognized and ranked. Some institutions, such as Bogazici University and Istanbul Technical University, are highly regarded in international rankings.
The primary language of instruction is Turkish. However, many universities offer programs in English, especially at the graduate level. Language preparation courses are also available.
Yes, Turkey offers various scholarships for international students, such as the Türkiye Scholarships. Additionally, universities and external organizations provide scholarship opportunities.
Turkey is known for its relatively affordable cost of living compared to many Western countries. Living expenses, including accommodation, food, and transportation, are generally reasonable.
Istanbul, Ankara, and Izmir are popular choices for international students. Istanbul, in particular, offers a rich cultural experience and numerous universities.




I need to free scholarship
Me too!
I need to free scholarship
I want free admission in turkey…
I want a free schollership
I’m grade 12 Ethiopia student and i need free scholarship but I’m learn in national school